16 Products
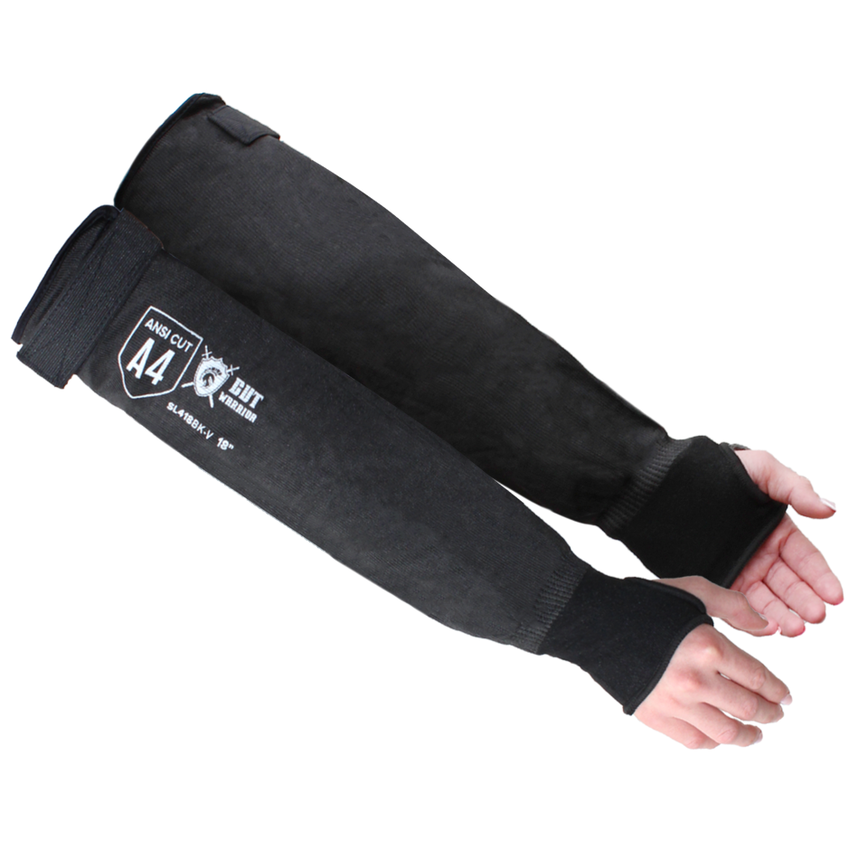
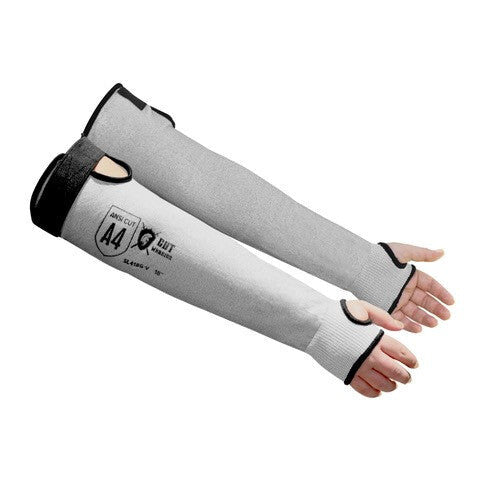
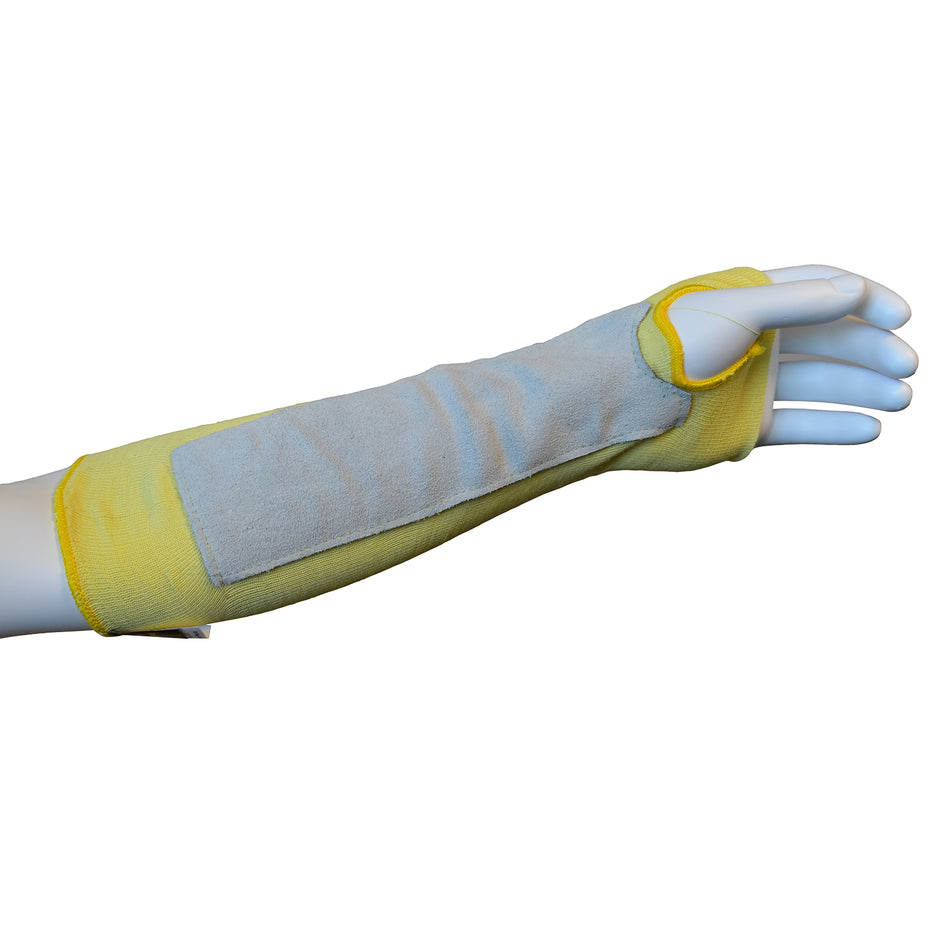
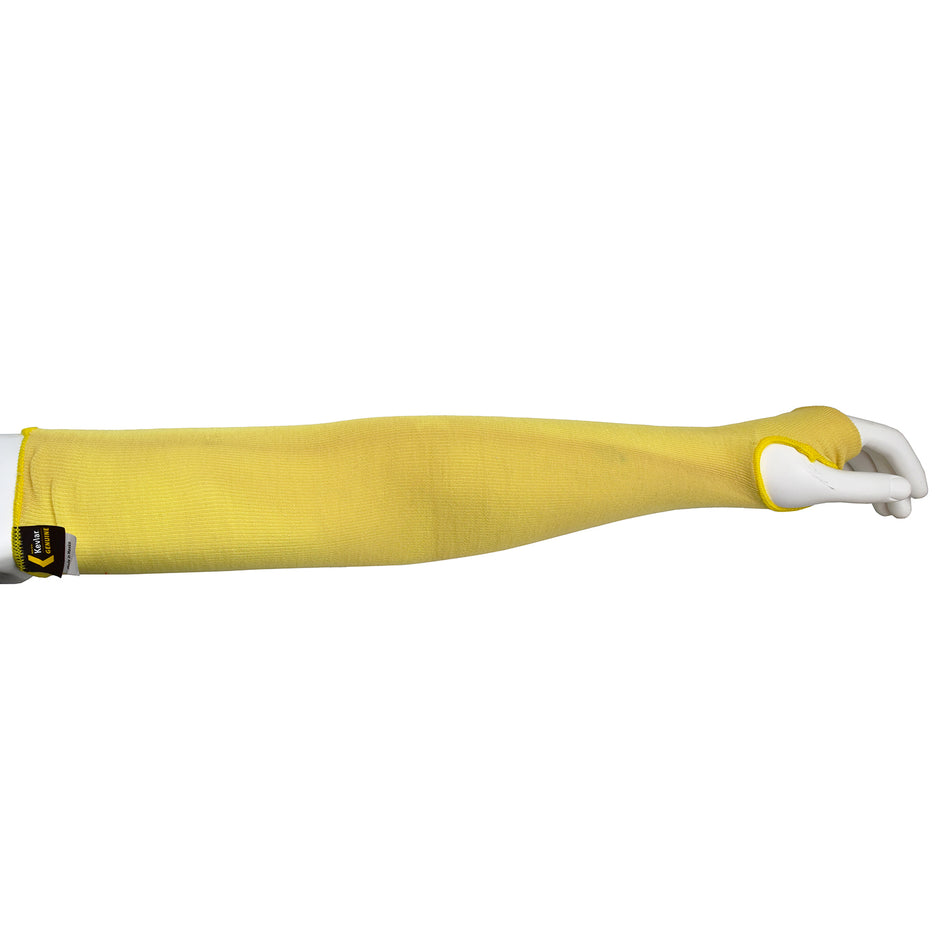
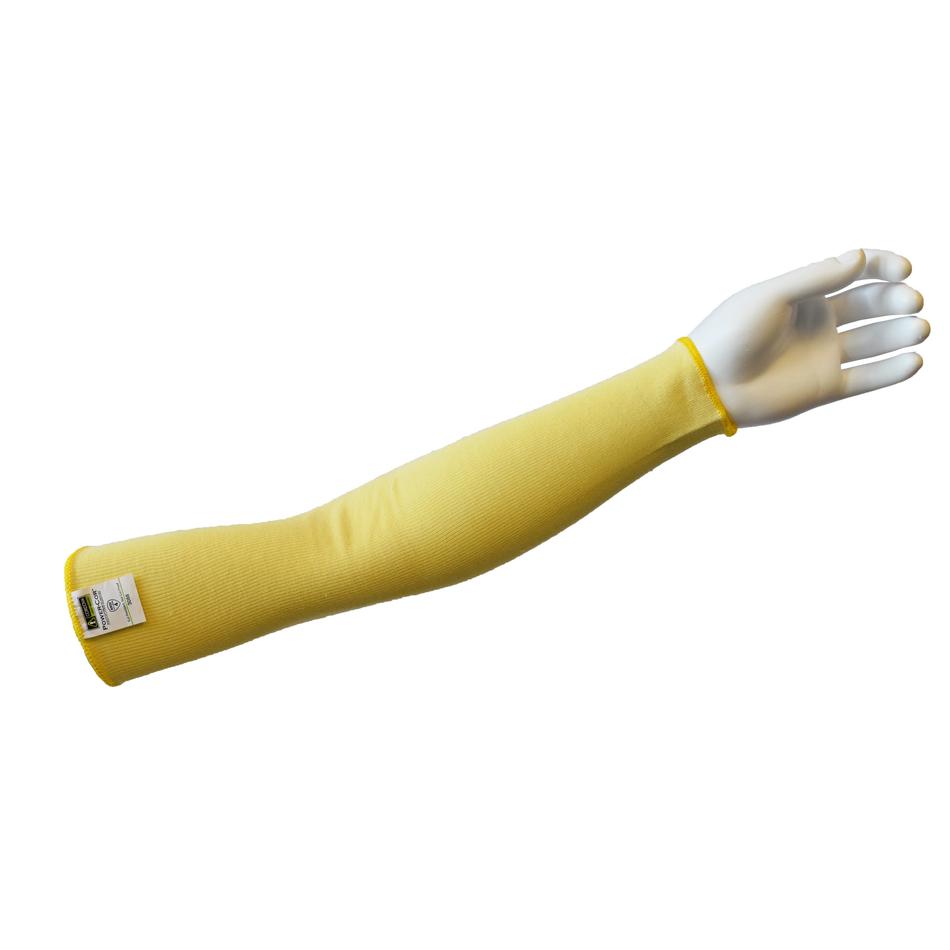
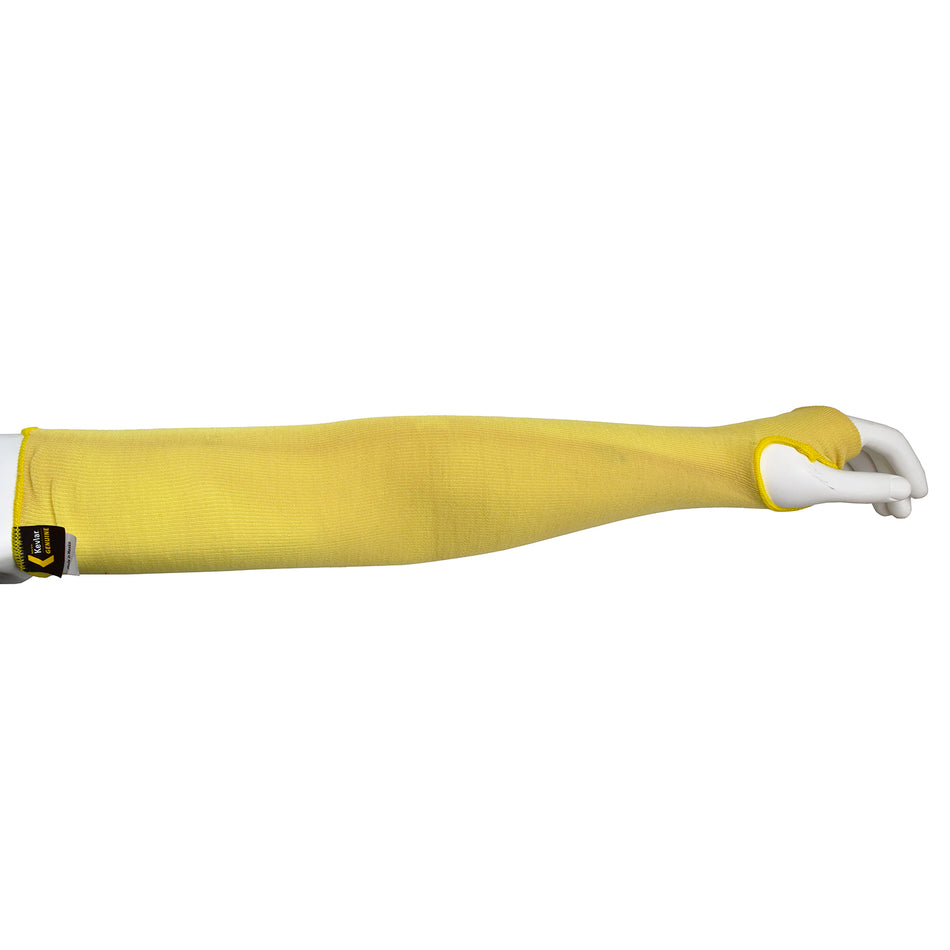
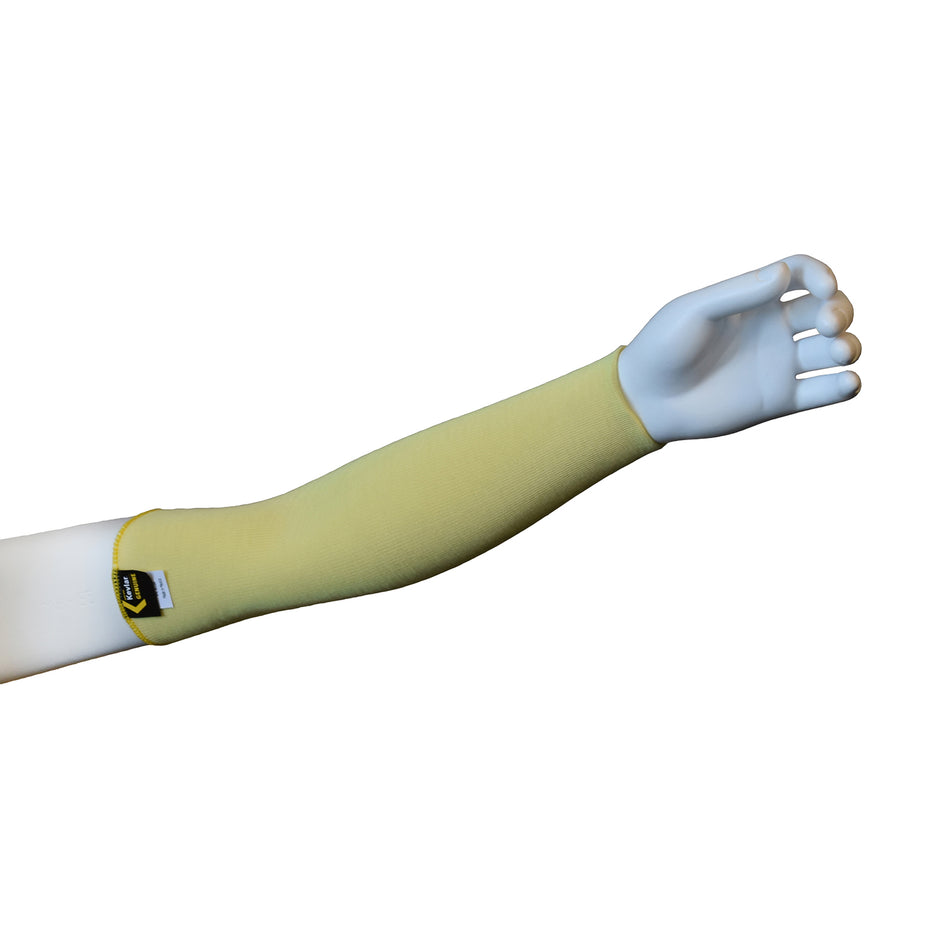
Cut Resistant Sleeve
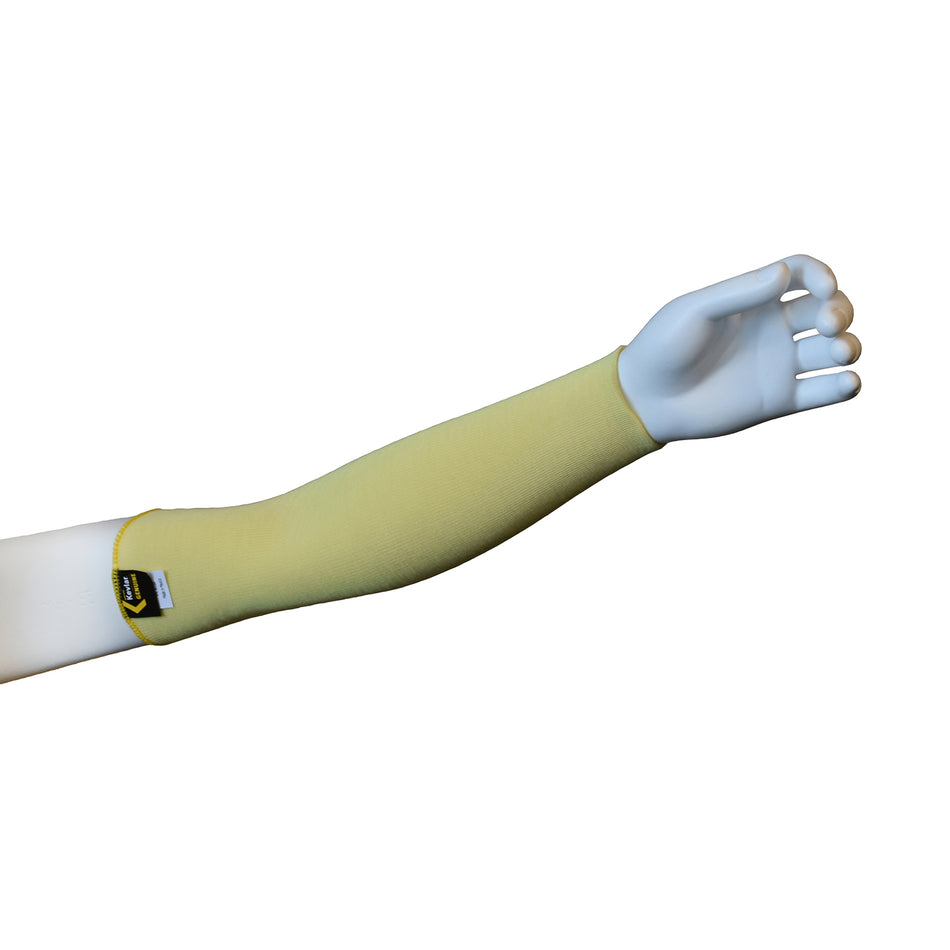
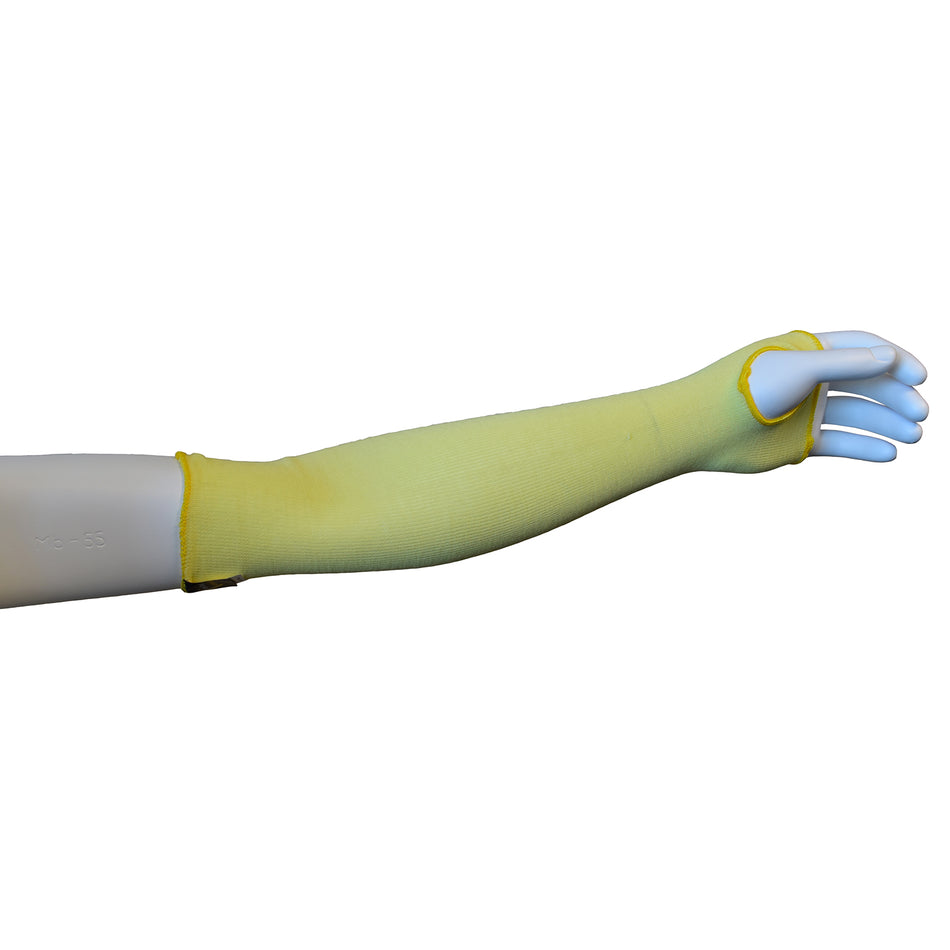
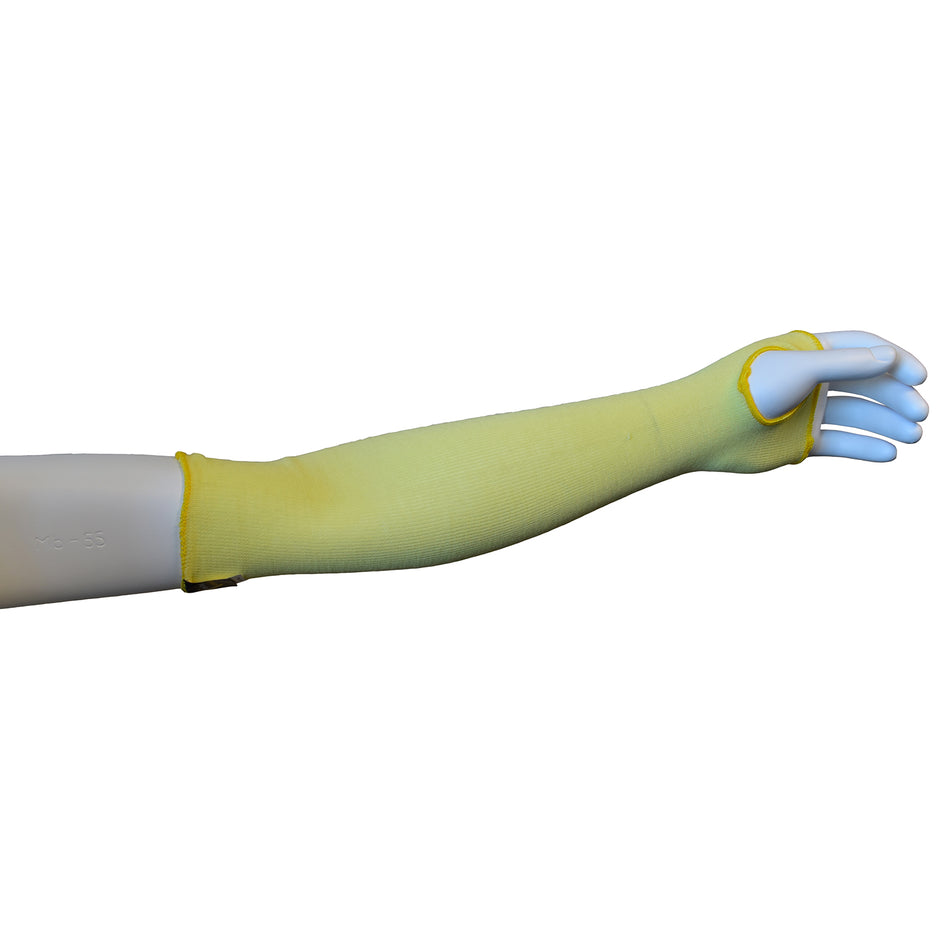
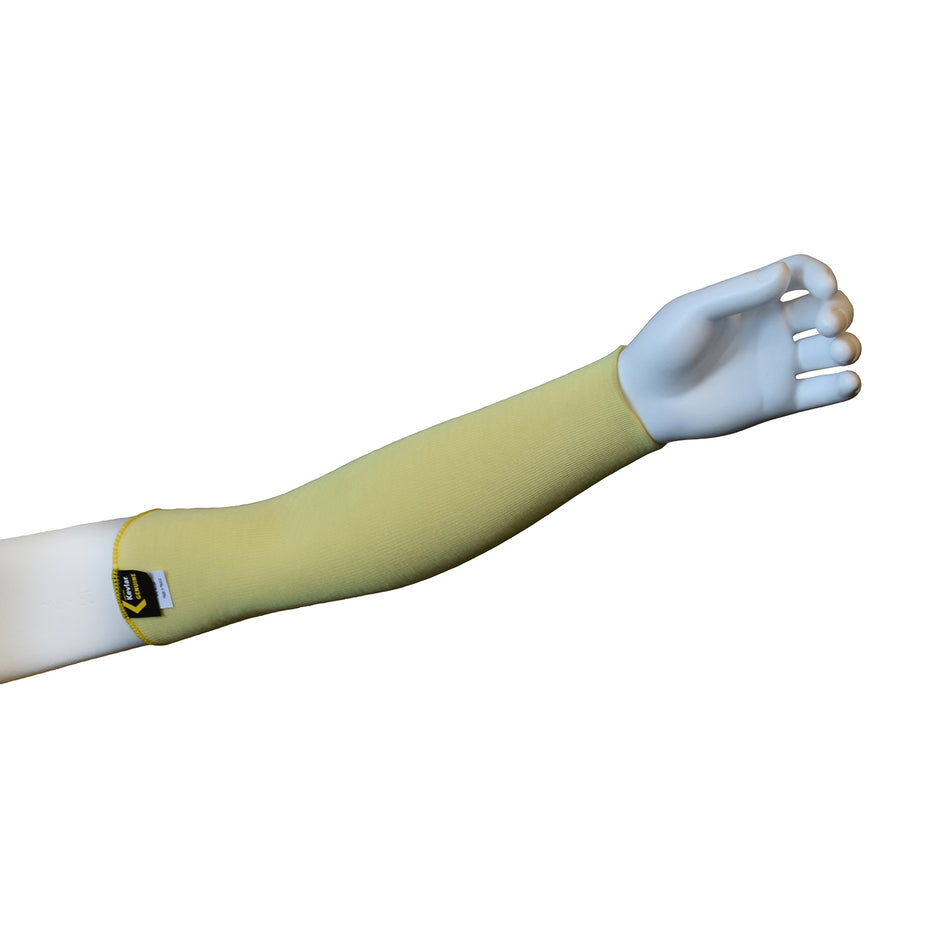
A cut-resistant sleeve is a protective arm covering designed to guard against lacerations, abrasions, and punctures during high-risk tasks.
Cut resistant sleeves are essential safety gear designed to protect workers' arms from cuts, scrapes, and punctures in demanding work environments. At Inland Empire Safety & Supply, we offer high-quality cut resistant sleeves made from durable materials like Kevlar, providing superior protection without sacrificing comfort. These sleeves are perfect for industries where workers frequently handle sharp or abrasive materials, such as metal fabrication, glass handling, automotive assembly, and food processing.
Designed to shield the forearms and upper arms, our cut resistant sleeves are available in various lengths, thicknesses, and ANSI cut resistance levels—ranging from ANSI A2 for light protection to ANSI A4 for high-risk tasks. With a secure, comfortable fit, these sleeves allow workers to perform their tasks with confidence.
Product Features
-
Firstly, made from durable materials like Kevlar for superior cut protection.
-
Secondly, available in various ANSI cut levels (A2, A3, A4) to suit specific tasks.
-
Thirdly, breathable, lightweight design ensures all-day comfort.
-
Fourthly, elastic cuffs prevent slipping for a secure fit.
-
Lastly, suitable for both forearm and full-arm protection.
Cut Resistant Sleeve Common Applications
-
Metal Fabrication: Protects against sharp metal edges and abrasive surfaces.
-
Glass Handling: Shields arms from glass shards and sharp edges.
-
Automotive Assembly: Provides cut protection when working with tools and parts.
-
Food Processing: Protects against cuts from knives and sharp tools.
-
Industrial Maintenance: Ensures safety when handling sharp or rough materials.
Safeguard your arms with premium cut resistant sleeves from Inland Empire Safety & Supply—trusted protection for workers in high-risk environments.